Prediction of COVID-19 with Statistical Data on Chest Radiography using Artificial Intelligence
Keywords:
Prediction, Artificial intelligence (AI), Chest radiography, COVID-19, Statistical dataAbstract
Introduction: COVID-19 is rapidly spreading around the world and has a high mortality rate. Artificial intelligence (AI) technology is a method that can be used to diagnose the presence of COVID-19 via chest radiographic apparatus. AI can be found to provide accurate results and increased diagnostic efficiency.
Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of artificial intelligence for COVID-19 diagnosis using statistical data from radiographic chest images.
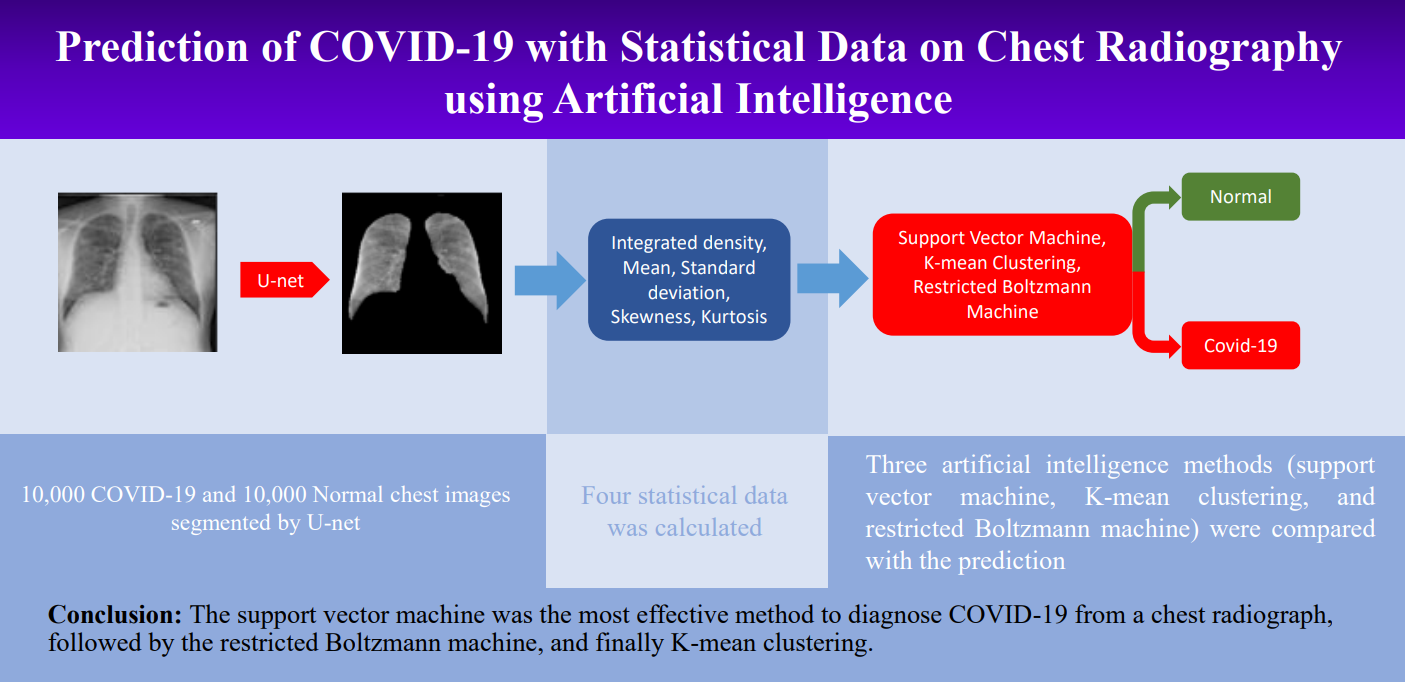
Methods: The research population sample consisted of 10,000 normal heathy individuals and 10,000 COVID-19 chest radiographs of patients were used for training (70.0%), validating (20.0%), and testing (10.0%). The images were segmented into the left and right lung regions by using the U-net architecture and then statistical data was calculated, including integrated density, mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis. Three artificial intelligence methods (support vector machine, K-mean clustering, and restricted Boltzmann machine) were compared the models’ predictions. The performance of three methods were analyzed for accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1-score.
Results: The accuracy of the support vector machine, K-mean clustering, and restricted Boltzmann machine were 70.5%, 62.5%, and 63.2%, respectively. The trend of the sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1-score were similar in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F1-score of the support vector machine, which were 64.2%, 73.5%, 68.2%, and 68.5%, respectively.
Conclusions: The most successful technique for diagnosing COVID-19 from chest radiographs was the support vector machine. It outperformed the restricted Boltzmann machine, which was followed by K-mean clustering
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19-20 April 2022. Geneva: WHO. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-COVID-19---20-april-2022. Published 2022. Accessed April 28, 2022.
World Health Organization. Use of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 self-testing (2022). Geneva: WHO. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Ag-RDTs-Self_testing-2022.1 Published 2022. Accessed April 28, 2022.
Hassantabar S, Ahmadi M, Sharifi A. Diagnosis and detection of infected tissue of covid-19 patients based on lung x-ray image using convolutional neural network approaches. Chaos Solit Fractals. 2020;140:110170.
Sethy PK, Behera SK. Detection of coronavirus disease (covid-19) based on deep features. Prepr. 2020:2020030300.
Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep Learning at Chest Radiography: Automated Classification of Pulmonary Tuberculosis by Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Radiology. 2017;284(2):574-582.
Ni Q, Sun Z Y, Qi L, Chen W, Yang Y, Wang L, et al. A deep learning approach to characterize 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia in chest CT images. Eur Radiol. 2020;30:6517-6527.
Kumar R, Arora R, Bansal V, Sahayasheela V J, Buckchash H, Imran J, et al. Accurate prediction of COVID-19 using chest x-ray images through deep feature learning model with SMOTE and machine learning classifiers. medRxiv. 2020;20063461.
Liu B, Gao X, He M, Lv F, Yin G. Online COVID-19 diagnosis with chest CT images: Lesion-attention deep neural networks. medRxiv. 2020;20097907.
Ibrahim D M, Elshennawy N M, Sarhan A M. Deep-chest: multi-classification deep learning model for diagnosing COVID-19, pneumonia, and lung cancer chest diseases. Comput Biol Med. 2021;132:1-13.
Yang D, Martinez C, Visuña L, Khandhar H, Bhatt C, Carretero J. Detection and analysis of COVID-19 in medical images using deep learning techniques. Sci Rep. 2021;11:1-13.
Das AK, Kalam S, Kumar C, Sinha D. TLCoV-An automated Covid-19 screening model using transfer learning from chest x-ray images. Chaos Solit Fractals. 2021;144:110713.
Joshi RC, Yadav S, Pathak VK, Malhotra HS, Khokhar HVS, Parihar A, et al. A deep learning-based COVID-19 automatic diagnostic framework using chest X-ray images. Biocybern Biomed Eng. 2021;41(1):239-254.
Khan MA. An automated and fast system to identify COVID-19 from X-ray radiograph of the chest using image processing and machine learning. Int j Imaging Syst Technol. 2021;31(2):499-508.
COVID-19 Radiography Database. Kaggle Inc. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/tawsifurrahman/covid19-radiography-database. Published 2022. Accessed April 28, 2022.
Google colaboratory. Google Research.colab.research.google.com Published 2022. Accessed April 28, 2022.
Pandey N. Lung segmentation from Chest X-Ray dataset. Kaggle Inc. https://www.kaggle.com/code/nikhilpandey360/lung-segmentation-from-chest-x-ray-dataset/notebook. Published 2022. Accessed April 28, 2022.
Pyradiomics. Radiomics features, https://www.pyradiomics.readthedocs.io. Published 2016. Accessed December 12, 2023.
Nour M, Cömert Z, Polat K. A novel medical diagnosis model for COVID-19 infection detection based on deep features and Bayesian optimization. Applied Soft Computing. 2020;97:106580.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Asian Medical Journal and Alternative Medicine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.


